Solid State Drives Inner Workings And Diverse Varieties
Hello, friends! this post will talk about How solid state drive Work and enable you guys to know the Types and Operation of SSDs
Catalog
What are solid state drive?
History
Structure and composition
Types
Classification
How Do SSDs Work? The Inner Workings, Explained
What are the advantages of a solid state drive (SSD)?
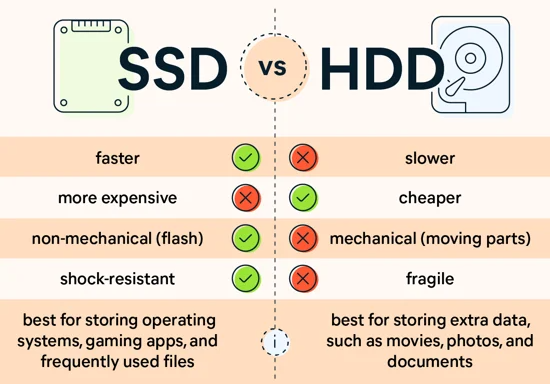
What is the difference between a hard drive and an SSD?
Solid state drives (SSDs) have revolutionized the storage industry with their speed, reliability, and efficiency. Unlike traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) that use spinning platters and magnetic storage, SSDs rely on flash memory to store data. In this article, we will explore how SSDs work, their types, operation, and delve into their history, structure, and composition.
**What are Solid State Drives?**
![308133759d6b7d70f8b1cbaa3c155c21.png 1EL3}T7({NG[V)I8{L97I]4](/upload/image/content/20240228/308133759d6b7d70f8b1cbaa3c155c21.png)
Solid state drives, as the name suggests, are storage devices that use solid-state memory to store data. They do not have any moving parts, unlike HDDs, which makes them more durable and less prone to mechanical failures. SSDs are known for their fast read and write speeds, low power consumption, and silent operation.
**History**
The concept of solid state storage dates back to the 1950s when early forms of solid-state memory were developed. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s and early 2000s that SSDs started to gain popularity in consumer electronics and computer systems. Advances in flash memory technology, along with improvements in controller technology, have made SSDs more affordable and widely adopted in recent years.
Here's a brief history of solid-state drives (SSDs):
- 1950s: The concept of solid-state storage emerged in the 1950s, but it was primarily limited to experimental and research purposes.
- 1970s: The development of semiconductor technology in the 1970s laid the foundation for the modern SSD. Companies like Texas Instruments and StorageTek introduced early forms of solid-state memory devices.
- 1980s: In the 1980s, the first commercial SSDs were introduced. These early SSDs used volatile memory known as SRAM (static random-access memory) and were predominantly used in specialized applications, such as military and aerospace systems, due to their high cost.
- 1990s: The 1990s saw advancements in non-volatile memory technologies, particularly NAND flash memory. NAND flash, which stores data even when power is removed, became the dominant type of memory used in SSDs. However, SSDs remained expensive and were primarily used in niche applications.
- Early 2000s: In the early 2000s, SSDs started to gain wider adoption in enterprise and industrial sectors due to their reliability and performance advantages over traditional hard drives. However, they were still prohibitively expensive for consumer use.
- Mid-2000s: Around the mid-2000s, as the cost of NAND flash memory started to decline, SSDs became more affordable and viable for consumer devices. Companies like SanDisk and Samsung introduced consumer-focused SSDs, primarily targeting the laptop market.
- Late 2000s: The late 2000s witnessed further advancements in SSD technology, including increased storage capacities and improved performance. SSDs started to gain popularity in high-end laptops and desktops as a faster and more reliable alternative to traditional hard drives.
- 2010s: Throughout the 2010s, SSDs continued to evolve, with increasing storage capacities and decreasing costs. The demand for SSDs grew significantly, and they became a standard feature in many laptops and desktop computers. The introduction of PCIe-based SSDs further accelerated their performance and made them suitable for demanding applications like gaming and content creation.
- Present: SSDs have become commonplace in various devices, including laptops, desktops, servers, gaming consoles, and even smartphones. They offer faster data access speeds, improved durability, energy efficiency, and compact form factors. SSDs continue to advance, with technologies like 3D NAND, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) interfaces, and QLC (Quad-Level Cell) flash memory pushing the boundaries of storage performance and capacity.
The history of SSDs demonstrates a progression from experimental technologies to mainstream storage solutions, driven by advancements in semiconductor technology and the decreasing costs of flash memory.
**Structure and Composition**
An SSD comprises three main components: flash memory chips, a controller, and a cache. The flash memory chips store the data in a non-volatile manner, meaning the data is retained even when the power is turned off. The controller manages the data flow between the flash memory and the host system, optimizing read and write operations for better performance. The cache, typically made of DRAM or SLC NAND, acts as a buffer to temporarily store data before writing it to the flash memory.
**Common Types**
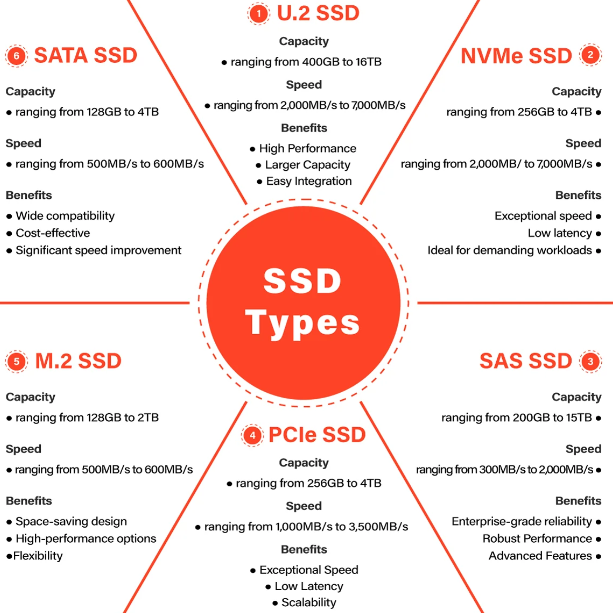
There are several types of SSDs based on the type of flash memory used and the form factor. The most common types include:
1. **SATA SSDs**: These SSDs use the SATA interface and are designed to replace traditional HDDs in laptops and desktop computers.
2. **NVMe SSDs**: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs provide faster speeds compared to SATA SSDs by using the PCIe interface for data transfer.
3. **M.2 SSDs**: M.2 SSDs are small, thin drives that connect directly to the motherboard via the M.2 slot, offering high-speed storage in a compact form factor.
4. **PCIe SSDs**: These SSDs use the PCIe interface for data transfer, offering even higher speeds than NVMe SSDs.
5. U.2 SSD
6. SAS SSD
In conclusion, solid state drives have redefined storage technology by offering high-speed performance, reliability, and efficiency. As flash memory technology continues to evolve, we can expect SSDs to become even faster and more affordable, making them the storage solution of choice for modern computing systems.
Classification
Solid-state drives (SSDs) can be classified in various ways based on different criteria. Here are some common classifications for SSDs:
1. **Based on Connection Interface**:
- **SATA SSDs**: These SSDs use the SATA interface, which is common in older systems.
- **NVMe SSDs**: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs use the NVMe protocol and typically connect via PCIe slots, offering faster speeds compared to SATA SSDs.
2. **Based on Form Factor**:
- **2.5-inch SSDs**: These SSDs have a form factor similar to traditional hard drives and are commonly used in laptops and desktop computers.
- **M.2 SSDs**: M.2 SSDs are smaller and connect directly to the motherboard through an M.2 slot. They are often used in laptops and small form factor desktops.
3. **Based on Technology**:
- **SLC (Single-Level Cell) SSDs**: These are the fastest and most durable SSDs, but they are also the most expensive.
- **MLC (Multi-Level Cell) SSDs**: These are more common and offer a balance between speed, endurance, and cost.
- **TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs**: These SSDs are cost-effective but typically have lower endurance and performance compared to SLC and MLC SSDs.
- **QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs**: These SSDs are designed for high capacity and cost efficiency but may have lower performance and endurance.
4. **Based on Use Case**:
- **Consumer SSDs**: These are designed for everyday consumer use, offering a balance of performance and price.
- **Enterprise SSDs**: These SSDs are optimized for server and data center use, focusing on performance, reliability, and endurance.
- **Industrial SSDs**: These SSDs are built to withstand harsh environments and operate in industrial settings.
5. **Based on Endurance**:
- **Consumer-Grade SSDs**: These SSDs are designed for typical consumer workloads and have lower endurance compared to enterprise-grade SSDs.
- **Enterprise-Grade SSDs**: These SSDs are built for heavy workloads and offer higher endurance and reliability.
Can a laptop have both SSD and HDD?
Can we use 'hard drive' phrase for SSD?
How Do SSDs Work? The Inner Workings, Explained
How do solid state drives (SSD) store and retrieve data?
SSD vs. HDD: How to choose?
What are the advantages of a solid state drive (SSD)?
What is an SSD (Solid State Drive)?
What is the difference between a hard drive and an SSD?

Frequently Asked Questions


















