Circuit For Buck Boost Converters: Stable Transforming Voltage

Hello guys, Today we are going to see the introduction of the Buck-boost converter. Buck-boost converters are a form of switching-mode power supply. It can supply a regulated DC output from a source voltage either above or below the desired output voltage. This can be particularly helpful in battery-powered applications in which the battery voltage starts out above the desired output but falls below as the battery drains. It’s useful for every engineer to understand the fundamentals of Buck-Boost Converter.
Catalog
1. Conceptual overview
2. What exactly is a Buck Converter?
3. What exactly is a Boost Converter?
4. What exactly is a Buck-Boost Converter?
5. Modes of Buck Boost Converters
6. Circuit of Buck Boost Converters
7. Where can buck boost converter can be used?
8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a buck converter?
1. Conceptual overview
The operation of a buck-boost converter can be understood by considering the inductor's reluctance to allow rapid changes in current. Initially, when the switch is open, there is no current through the inductor. When the switch is closed, the blocking diode prevents current from flowing into the right side of the circuit, causing all the current to flow through the inductor. However, the inductor limits the current change by dropping most of the voltage supplied by the source.
Over time, the inductor gradually decreases its own resistance, allowing the current to slowly increase. In an ideal circuit, the voltage drop across the inductor remains constant. However, when the inherent resistance of the wires and switch is considered, the voltage drop across the inductor also decreases as the current increases. Meanwhile, the inductor stores energy in the form of a magnetic field.
For many years, switch-mode power conversion has been a pillar of modern electronics technology in numerous areas, including utility, industrial, commercial, and consumer industries. Most modern power conversion in low-power DC/DC conversion applications is done with three main types of power converters: Buck, Boost, and Buck-Boost Converters. This article looks at the principles of each sort of converter, where they might be utilized in practice and the advantages and disadvantages.
2. What exactly is a Buck Converter?
Definition: A buck or step-down converter is a DC/DC switch mode power supply designed to buck (or reduce) an unregulated DC supply's input voltage to a stabilized lower output voltage. Buck converters are highly prized for their extraordinarily high efficiency, which can easily reach 95% when compared to ordinary voltage regulators. The simplified circuit schematic below depicts how current flows across the circuit during a buck converter switching event.

Buck converters are frequently used to provide low-voltage on-board power in a range of applications such as microprocessors, communication equipment, control systems, and more, in place of traditional, inefficient linear regulators.
3. What exactly is a Boost Converter?
Definition: A boost converter is a DC/DC switch mode power supply created to boost (or increase) an unregulated DC supply's input voltage to a stabilized higher output voltage. A boost converter, like a buck converter, uses an inductor, diode, capacitor, and power switch to adjust the output voltage, but they are organized differently. The simplified circuit schematic below depicts how current travels through the circuit during a boost converter switching event.

4. What exactly is a Buck-Boost Converter?
A buck-boost boost converter can supply a regulated DC output from a power source delivering a voltage either below or above the regulated output voltage. A buck-boost converter circuit combines elements of both a buck converter and a boost converter, however they are often larger in footprint than either alternative. The below simplified circuit diagram shows a typical flow of current during a switching event through a buck-boost converter.

As you may have noticed in the circuit diagram, V out is actually negative with respect to the supply potential, which can complicate certain designs. Buck-boost converters also require more expensive components as they need to withstand both high Vin max voltage and high input current at Vin min, but they are useful in many applications. A very common use of buck-boost converters are for high power LED lighting where, for example, lead-acid batteries supply a nominal 9-14V to a constant 12V LED load.
Conclusion
The technology of buck, boost, and buck-boost converters are utilized around the world to provide regulated low-voltage DC/DC power in nearly every electronics market. Xinshop’s buck, boost, and buck-boost converters are an excellent solution for your low-power conversion needs.
5. Modes of Buck Boost Converters
There are two different types of modes in the buck boost converter. The following are the two different types of buck boost converters.
lContinuous Conduction Mode:
The current from end to end of inductor never goes to zero. Hence the inductor partially discharges earlier than the switching cycle.
lDiscontinuous Conduction Mode
The current through the inductor goes to zero. Hence the inductor will totally discharge at the end of switching cycles.
6. Circuit and wave of Buck Boost Converters

The input voltage is 100 V DC and the duty cycle is 0.5.
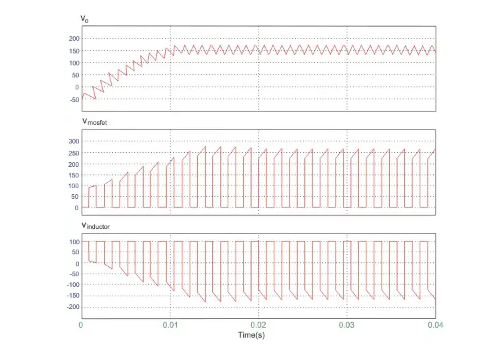

The voltage waveforms
7. Where can buck boost converter be used?
A.A buck converter is used to reduce the voltage of a given input in order to get the desired output.Buck converters are most commonly found in USB on the go, point of load converters for PCs and laptops, battery chargers, quad copters, solar chargers, and power audio amplifiers.
B. Boost converters are used in electronics to provide a DC output voltage greater than the DC input voltage, thus increasing the supply voltage. Boost converters are frequently found in power supply for white LEDs, battery packs for electric vehicles, and a variety of other applications.
C. Applications of Buck boost converter
It is used in the self regulating power supplies.
It has consumer electronics.
It is used in the Battery power systems.
Adaptive control applications.
Power amplifier applications.
8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a buck converter?
Current Mode Buck Converters
Advantages
Stable fixed frequency Can be Synchronized to
ext. clock Established technology Stable with MLCC.
Disadvantages
Slow response to fast load steps Needs error
amplifier compensation Needs slope compensation

Frequently Asked Questions


















