Electronic Components in Mobile Phones and the Chip Shortage Impact

This post will briefly introduce the Electronic Components in Mobile Phones and the Chip Shortage Impact
Introduction:
The introduction will provide an overview of the topic, highlighting the significance of electronic components in mobile phones and the current challenges posed by the chip shortage. It will set the stage for the subsequent sections and establish the importance of understanding the multitude of electronic components and their impact on mobile phone production.
1. The Multitude of Electronic Components in Mobile Phones:
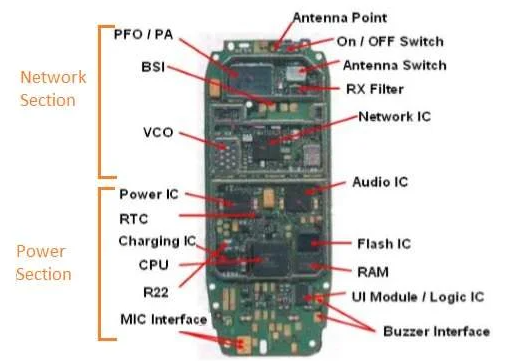
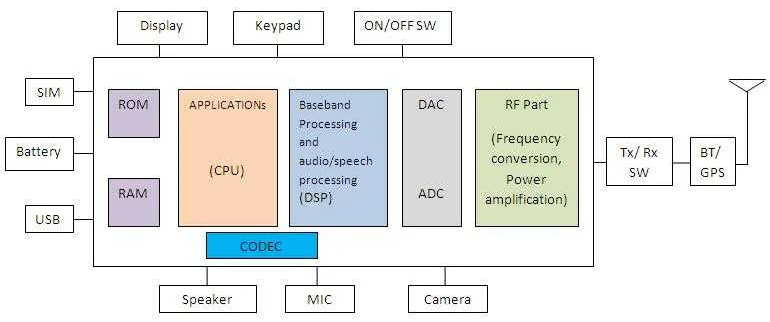
Now let's will delve into the vast array of electronic components found in mobile phones, providing comprehensive explanations of each component's function and significance. It will cover processors (CPU and GPU), memory components (RAM, ROM, and flash memory), communication modules (baseband processors, modems, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS), display and touchscreen components, power management components, camera components, audio components, sensing components, and miscellaneous components.
2. The Impact of the Chip Shortage on Mobile Phones:
This section will explore the far-reaching consequences of the global chip shortage on the mobile phone industry. It will discuss the repercussions for manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers, including production delays, decreased supply, increased prices, reduced innovation and development, and potential long-term effects on the industry.
For manufacturers, the chip shortage has forced many to drastically cut production targets for 2022. Companies like Samsung, Xiaomi and Oppo have reduced output by tens of millions of units compared to plans. This has squeezed revenue and profits. Supply chain disruptions have also hampered efficiency and increased costs.
Component suppliers serving the phone industry have also felt the effects. Semiconductor foundries like TSMC have been unable to satisfy demand from major customers. Specialized firms making modems, displays or other smartphone chips have had order backlogs grow significantly. This threatens the financial viability of some smaller players.
Consumers are seeing limited availability of popular phone models across regions. Prices have risen as well to account for increased component costs and manufacturer margins. Upgrades are taking longer as customers hold onto existing devices longer during the shortage.
Perhaps most worrying is the impact on research and development budgets. With profits hit, manufacturers have less to reinvest in next-gen technology and innovation. This risks slowing advancement in areas like 5G, AI capabilities, display tech and more. Delays to launching cutting-edge phones could harm competitiveness long-term.
The knock-on socioeconomic influence should also not be ignored. Sectors dependent on the smartphone industry are suffering reduced activity. Jobs across design, manufacturing and retail may be damaged due to sustained lower production levels in 2022-23.
For the broader tech landscape, deficiencies in the semiconductor supply chain have exposed vulnerabilities. Future disruption could be minimized through alternative suppliers, local sourcing strategies and stockpiling key components. However, the complete effects of the ongoing shortage may not emerge for years ahead.
3. What is a Chip and Why is it Important:
A chip is an integrated circuit that controls electrical signals and data processing in all modern electronics. Mobile phones require numerous chips for functions like processing, graphics, connectivity, storage and more. It will cover integrated circuits, semiconductor materials, transistor technology, and the role of chips in processing data, storing information, and enabling communication. The significance of chips in enhancing mobile phone performance, functionality, and efficiency will be emphasized.
There are two main chip types - memory chips that store data and program instructions, and logic chips that perform calculations and run code. Logic chips in phones include the applications processor, baseband processor and integrated discrete components.
The ongoing global chip shortage has significantly disrupted phone production lines. Lockdowns triggered a surge in work-from-home electronics demand. As people bought new devices, chip foundries struggled to keep up with orders.
Supply chain disruptions and factory shutdowns further exacerbated the problem. Now many phone makers have limited components to fully assemble models. Others face delays in shipping new releases as chip deliveries are delayed.
Phones require dozens of different chips each made on specialized production lines with lead times of 6-12 months. Shortfalls cannot be quickly solved by seeking alternative suppliers. Prices for certain mobile chips have risen over 20% due to tight supply.
While top brands can negotiate to prioritize their allocations, smaller phone companies have been heavily impacted. Some inexpensive 5G handsets and accessory lines have been temporarily cancelled until chip availability improves later in 2022.
The shortage highlights mobile phones' reliance on an intricate global semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem. Building additional fab capacity and diversifying suppliers could help boost future chip resilience for the electronics industry.
4. The Classification of Chips:
Let's categorize chips based on their functions and capabilities. It will discuss different types of chips found in mobile phones, such as processors (CPUs and GPUs), memory chips (RAM, ROM, and flash memory), communication chips (baseband processors, modems, wireless modules), power management chips (PMICs), camera chips (image sensors, ISPs), audio chips (codecs), sensing chips (accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers), and miscellaneous chips (SIM card slots, USB ports, antennas).
5. Why Chips are in Shortage:
Underlying reasons for the chip shortage, including increased demand for electronic devices, supply chain disruptions, geopolitical factors, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. It will highlight the complexities and interdependencies within the global chip supply chain, leading to imbalances in supply and demand.
6. Where Can I Find Chips:
Here are some suggestions for where to find chips during the ongoing shortage:
Contact component distributors directly: Large distributors like Mouser, DigiKey and Arrow have regular inventory updates online. Sign up for in-stock notifications. Some may prioritize larger customers.
And also Xinshop is a leading global trader and supplier of electronic components. Founded in 2012, our company has many years experience of sourcing and supplying a wide range of electronic components to customers worldwide. Please feel free to contact us!
Check specialty retailers: Retailers focused on hobbyist projects and maker communities like Adafruit and SparkFun often have limited chip supplies. Order sooner than later.
Search chip broker sites: Aggregators like chipbroker.com connect buyers with sellers who have excess inventory from cancelled orders. Prices may be higher.
Try industrial equipment surplus: Surplus liquidators of used semiconductor manufacturing and testing equipment sometimes sell individual chips in bulk volumes.
Contact chip manufacturers directly: Email sales teams at chip companies like Microchip, STMicroelectronics, NXP, etc. to inquire about small order quantities if part of a design project.
Monitor auction sites: Search eBay, Alibaba for chips listed in small lots from second-source suppliers globally. Prices tend to fluctuate wildly.
Network for local surplus: Engineering schools, repair shops may offload unused parts. Check community forums, local classifieds.
Consider chip alternatives if possible: Look for functional equivalents with similar specs that may have better availability currently.
Sourcing chips remain challenging but exploring diverse procurement channels can uncover limited stock during shortages.
7. Conclusion and Suggestions:
The conclusion will summarize the key points discussed in the article, emphasizing the importance of electronic components in mobile phones and the significant impact of the chip shortage. It will highlight the need for industry collaboration, investment in domestic chip production, diversification of suppliers, and improved transparency and communication within the supply chain. It will also provide recommendations for individuals and businesses navigating the chip shortage and its implications.


















