Uncovering the Secrets of Electronic Component Storage
Today this article will lead you to explore the preservation period of electronic components and storage conditions , storage temperature and handy tips to protect the electronic parts,which will enables prolonging the life of the parts.
Catalogue:
1. Introduction
2. Factors affecting the storage of electronic components
3. Tips and tricks to extend the life of components
4. Conclusion

1. Introduction
Electronic components are the key support for the development of modern science and technology, and their preservation is vital for engineers, electronics enthusiasts and technology enterprises. Nowadays, whether in the global or Chinese market, the rapid growth in the sales of new energy vehicles and intelligent vehicles will drive a new peak in the demand for chips. The actual situation of chip production now is that, on the one hand, chip manufacturers continue to enhance production capacity, and the production situation is gradually improving; on the other hand, the demand for chips is strong, and there will also be a shortage of supply.
Many consumers, however, are unaware that proper storage procedures and environmental conditions can increase the life of components and maintain their performance consistent. We will reveal the mysteries of electronic component storage and teach you how to scientifically preserve these valuable technological gems - electronic components - in this post.

2. Factors Affecting the Storage of Electronic Components
Each component has its own characteristics, in which the key factors affecting its storage time is the chemical reaction with moisture, oxygen, sulfur and other impurities in the air, as well as temperature, such as electrolytic capacitors in a high-temperature environment electrolyte will dry up and so on. If the vacuum packaging, in a constant temperature environment, electronic components storage time is quite long. Place: Ventilation, dry, no corrosive gas. Warehouse to maintain ventilation, light, ventilation, access to a smooth state, smoking is strictly prohibited, prohibit unauthorized use of fire, electricity and do a good job of fire prevention, fire signs clear.
Storage conditions and duration
A. No special requirements for qualified raw materials, semi-finished goods storage conditions: sunshade, room temperature, ventilation, dry.
B. Storage period
① The effective storage period of electronic components is 12 months;
② plastic parts of the effective storage period of 12 months;
③ The effective storage period of hardware is 6 months;
④ The effective storage period of packaging materials is 12 months;
⑤ The effective storage period of finished products is 12 months.
C. special requirements of the goods for special requirements of the materials stored in accordance with the storage requirements. Material category storage relative temperature storage relative humidity storage height, container storage period solder paste, glue class 2-10 ℃ constant temperature and humidity cabinet storage according to the shelf life of electronic components 20 ± 5 ℃ 40% ~ 70%.
The combination of storage temperature and humidity is the decisive factor. The combination of high humidity and high storage temperatures can cause components to absorb moisture or gases, even if stored for a short period of time.
For SMDs (Surface Mount Devices), moisture sensitivity is measured by the Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) defined by JEDEC standard J-STD-020:
MSL Rating Exposure Time Ambient Conditions
Unlimited 30°C/85%RH
1 year 30°C/60%RH
4 weeks 30°C/60%RH
68 hours 30°C/60%RH
72 hours 30°C/60%RH
48 hours 30°C/60%RH
24 hours 30°C/60%RH
TOL 30°C/60%RH
The "exposure time" is the time available after the sealed moisture-proof bag is opened, i.e., components can be reflowed without the risk of "popcorn phenomenon". If the device absorbs moisture during the exposure time it will turn into vapor in the hot oven causing the device to crack, delaminate or even explode. If the exposure time of a component exceeds the specified time, it needs to be "pre-baked". In other words, the device is placed in a drying oven to evaporate the absorbed moisture before use.TOL refers to the "Time of Labeling" indicated by the reference manufacturer.
2.1 Environmental Requirements:
Electronic components must be stored in a clean, ventilated, non-corrosive gases in the warehouse class indoor environment, the warehouse should be in the channel in a smooth state. Another storage of electronic components warehouse temperature and relative humidity must meet the following requirements: temperature: -5-30, relative humidity: 20%-75% RH, the warehouse environment temperature and humidity values will directly affect the storage life of electronic components and quality of quality.
The storage of electronic components has strict requirements for environmental temperature and humidity parameters.
2.2 Special Requirements:
2.2.1 electrostatic sensitive devices (such as MOS field effect transistors, gallium arsenide field effect transistors, CMOS circuits, etc.), should be stored in the storage equipment with the role of shielding static electricity;
2.2.2 Sensitive to magnetic fields but no magnetic shielding of its own electronic components, should be stored in the role of shielding magnetic field storage equipment;
2.2.3 Electromechanical originals with oil seals shall keep the oil seals intact.
2.3 Limited Storage Period :
Different grades of electronic components stored in the appropriate temperature and humidity parameters are not the same. class A device storage temperature and humidity values are: 15-25, 25%-60% RH; class B device storage temperature and humidity values are: -5-+30, 20%-75% RH; class C device storage temperature and humidity values are: -10-+40, 10%-80% RH.
2.4 Storage Requirements:
2.4.1 The electronic warehouse requires an anti-static floor, personnel must be in accordance with the requirements of anti-static, dressed in anti-static clothing, wearing anti-static bracelets;
2.4.2 Requirements according to the category of items stored in zones, flammable and explosive products require appropriate isolation measures, for special requirements of the items should have a significant warning signs or safety signs;
2.4.3The materials are neatly arranged, and the contents of the storage cards are standardized, so that the accounts, materials and cards are in line with each other;
2.4.4 Items can not be stored directly on the ground, need to have a tray or shelf protection;
2.4.5 Material stacking requirements on the small under the big, light under the heavy, a tray can only be placed on the same kind of material, stacking height has special requirements based on special requirements stacking, but the highest shall not exceed 160cm;
2.4.6 Bulk materials, tray materials and items with special requirements for storage specific reference to the relevant norms;
2.4.7 The items with anti-static requirements must be selected according to the actual situation of the following methods: loaded into anti-static bags and anti-static moisture-proof cabinet storage.
2.5 Raw Material Protection Requirements:
2.5.1 Electronic components should give full consideration to the requirements of dust and moisture resistance;
2.5.2For vacuum-packed PCB light board, IC, etc. to be intact packaging, can not let the copper foil and pins directly exposed to the air to prevent product oxidation;
2.5.3 For the protection of special raw materials, please protect them according to their requirements;
2.5.4. For components with pins, especially IC and other components whose pins are easy to be deformed, we should use the original packaging form to avoid the deformation of the component pins, which may cause inconvenience or even prevent the operation.
2.6 Ambient Temperature and Humidity Requirement
Temperature is a factor we want to discuss in detail. The effects of temperature Cycling of ambient temperatures also causes microcracks and seal failures. If a device is manufactured in a warm and humid climate and then shipped in the cargo hold of an airplane at -40°C, any internal moisture will break the seal as the ice expands. Devices go through different flight or road traffic distribution centers, so they may go through several thaw/freeze cycles before reaching their final destination, causing the malady to continue to grow. If the device then undergoes several winter and summer rotations in a non-temperature-controlled warehouse, less intense but more prolonged thermal cycling stresses may occur.
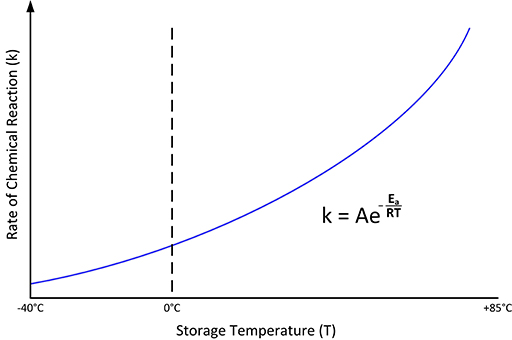
Assuming that the manufacturer states that the device can be stored in a temperature and humidity range of -40°C to +85°C and 50% RH, this does not mean that the device is safe from several temperature cycles within the storage temperature limits. The fact is that if the device is stored at low temperatures in order to minimize the aging process of the ions or atoms (Figure 3), it must be very slowly rewarmed before use. Continuous storage at low or high temperatures is more suitable for the storage of the components than several hot and cold cycles.
What happens if the storage temperature is exceeded? SMD devices mounted on PCBs do not have the same thermal expansion or contraction as the substrate itself, so mechanical stresses at extreme temperatures can cause solder to break or devices to rupture. Packaged components (diodes, transistors, etc.) can usually withstand lower temperatures because the housing provides mechanical support for the pins, but they generally have metal leadframes, and copper has a high coefficient of thermal contraction, so failures can occur at temperatures below -40°C.
At very low temperatures, the most difficult problems arise in devices that rely on ionic motion or liquid chemical processes, including electrolytic capacitors and some types of ceramic capacitors, because these activities are "frozen" at low temperatures.
Other devices sensitive to very low temperatures are wire-wound inductors and transformers. The copper windings in these devices will shrink at low temperatures and exert mechanical strain on the ferrite core, which becomes more fragile at low temperatures because the adhesive of the ferrite grains loses its elasticity. If a product containing a ferrite device is accidentally dropped at low temperatures, even if it is "securely" encapsulated in an adhesive sealer, it can be easily ruptured by mechanical shock (Figure 4), so care should be taken in handling products and accessories taken out of cold storage.
In summary, if a device or accessory is stored in a good environment that is relatively stable or slow to change, the shelf life is very long indeed. Under ideal conditions, RECOM's encapsulated DC/DC or AC/DC power modules have a shelf life of ten years. However, if such a product is put into service after a long period of storage, it should first be allowed to slowly acclimatize to room temperature and visually inspected to ensure that the pins and connectors are free of corrosion. If the product contains electrolytic capacitors, a limited amount of current should be applied to slowly power up the product (a process known as "reconfiguration") and allow the dielectric insulation of the aluminum oxide to recover before subjecting it to full input voltage.
Global supply chain issues nowadays have resulted in many distributors and suppliers needing to ship out old inventory to meet customer demand in a timely manner. With proper storage conditions and slow warming before power up, these components may still be in perfect condition for use.

3. Tips and tricks to extend the life of components
If you have to store components long-term, they should generally not be left out on the shelf in open air, even if the humidity and temperature conditions are appropriate. If you’re unsure as to the required storage conditions for specific components, check your component datasheets for appropriate packaging and environmental conditions.
Plastic bags - These are appropriate for most passives and moisture/ESD insensitive components. The bags that are appropriate for these components are non-triboelectric, meaning they tend to not accumulate static charge that would lead to ESD.
ESD protective bags - For ESD protection, there are conductive bags that can be used to store components. These bags can withstand a moderate ESD pulse that might otherwise harm a component. These bags can also be used to store or ship completed assemblies to customers.
Desiccants - A simple silicone desiccant is a low-cost material that can be used to absorb moisture in the event humidity in the surrounding environment becomes high. Dessicants can be placed inside plastic bags or ESD bags to provide targeted protection from humidity.
Vacuum seal bags - A simple solution to prevent moisture ingress is to vacuum seal components, typically with desiccant placed in the storage packaging. There are vacuum-sealable ESD protective bags for ESD-sensitive components.
Finally, if you really want to make sure your components will be safe, use the same packaging materials that were supplied by the manufacturer. One common example is for BGA packages on organic substrates; if these are purchased directly from a manufacturer, they could be vacuum sealed in an ESD protective bag and packaged with desiccant. This type of packaging and storage at appropriate temperature will protect against the three main component degradation factors of ESD, moisture, and high temperature.
By the way, if you want to purchase a large number of electronic components, please feel free to click the link below and contact us: Xinshop

4. Conclusion
Electronic components are an important cornerstone of technological development, and proper storage methods and environments are crucial to maintaining their performance. With the advice and tips provided in this article, you will be able to easily preserve your valuable technological treasures and utilize them in future projects and innovations. Take action today to make your electronic component inventory more organized and secure!


















