ATMEGA8A-AU Datahseet, Pinout, Specs, Price, Programming
yunying Release time:2024-03-18 Page View:391

ATMEGA8A-AU 8-bit Microcontrollers - MCU AVR 8KB, 512B EE 16MHz 1KB SRAM
Low-Power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller Data Sheet
- Introduction
- ATMEGA8A-AU Description
- ATMEGA8A-AU Features
- ATMEGA8A-AU Pinout
- ATMEGA8A-AU CAD-Model
- ATMEGA8A-AU Block Diagram
- ATMEGA8A-AU Alternatives
- ATMEGA8A-AU Appllications
- ATMEGA8A-AU How to program ATmega8 using USBasp?
- ATMega8A vs ATMega328p
- Related articles
- Specifications
- Datasheets
- Product comparison
Introduction
The ATmega8A is a low-power CMOS 8-bit microcontroller based on the AVR® enhanced RISC architecture. By executing powerful instructions in a single clock cycle, the ATmega8A achieves throughputs close to 1 MIPS per MHz. This empowers system designers to optimize the device for power consumption versus processing speed
ATMEGA8A-AU Description
The AVR® core combines a rich instruction set with 32 general purpose working registers. All the 32 registers are directly connected to the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), allowing two independent registers to be accessed in one single instruction executed in one clock cycle. The resulting architecture is more code efficient while achieving throughputs up to ten times faster than conventional CISC microcontrollers.
The ATmega8A is a microcontroller that offers several features, including 8 KB of programmable Flash memory, 512 B of EEPROM, 1 KB of SRAM, 23 general-purpose I/O lines, and 32 general-purpose working registers. It also includes three flexible timer/counters, internal and external interrupts, a serial programmable USART, a two-wire serial interface, and a 6-channel ADC with 10-bit accuracy. The microcontroller supports various power-saving modes, such as Idle mode, Power-down mode, Power-save mode, ADC Noise Reduction mode, and Standby mode, which allow for reduced power consumption while maintaining specific functionalities.
ATMEGA8A-AU Features
• It is a High-performance, Low-power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller and has Advanced RISC Architecture
– 130 powerful instructions - most single-clock cycle execution
– 32 x 8 general purpose working registers
– Fully static operation
– Up to 16 MIPS throughput at 16 MHz
– On-chip 2-cycle multiplier
• It has High Endurance Nonvolatile Memory segments
– 8 KB of In-System Self-programmable Flash program memory
– 512B EEPROM
– 1 KB internal SRAM
– Write/erase cycles: 10,000 Flash/100,000 EEPROM
– Data retention: 20 years at 85°C/100 years at 25°C(1)
– Optional boot code section with independent lock bits
• In-system programming by on-chip boot program
• True read-while-write operation
– Programming lock for software security
• Microchip QTouch®
It has library support
– Capacitive touch buttons, sliders and wheels
– QTouch and QMatrix acquisition
– Up to 64 sense channels
• Peripheral Features
– Two 8-bit timer/counters with separate prescaler, one compare mode
– One 16-bit timer/counter with separate prescaler, compare mode, and capture mode
– Real-time counter with separate oscillator
– Three PWM channels
– 8-channel ADC in TQFP and QFN/MLF package
• Eight channels 10-bit accuracy
– 6-channel ADC in PDIP package
• I/O and Packages
– 23 programmable I/O lines
– 28-lead PDIP, 32-lead TQFP, and 32-pad QFN/MLF
• The Operating Voltages are between 2.7 - 5.5V
• Speed Grades: 0 - 16 MHz
• Power Consumption at 4 MHz, 3V, 25°C
– Active: 3.6 mA
– Idle mode: 1.0 mA
– Power-down mode: 0.5 μA
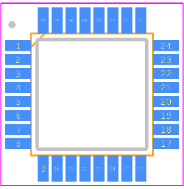
ATMEGA8A-AU Pinout

atmega8a-au tqfp32
ATMEGA8A-AU CAD-Model
Symbol
Footprint
3D-Model

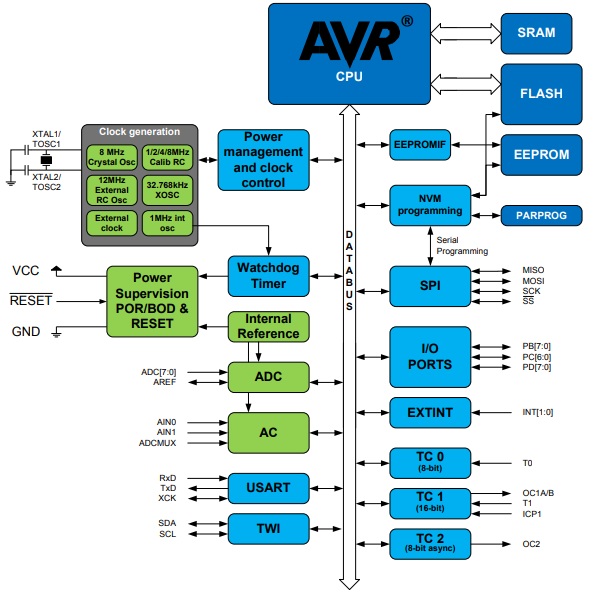
ATMEGA8A-AU Block Diagram
ATMEGA8A-AU Alternatives
ATMEGA8A-ANR, ATMEGA8A-AUR, ATMEGA8A-MN, ATMEGA8A-MNR, ATMEGA8A-MUR, ATMEGA8A-PN, ATMEGA8A-AU, ATMEGA8A-MU, ATMEGA8A-PU, ATMEGA8A-AN
atmega8a-au KynMTb atmega8a-au KaK npownTb
ATMEGA8A-AU Appllications
ATmega8A-AU microcontroller applications, including but not limited to:
- Embedded systems and control applications
- Home automation and IoT devices
- Robotics and automation systems
- Sensor interfaces and data acquisition systems
- Industrial control and monitoring systems
- Consumer electronics
- DIY projects and prototyping
ATMEGA8A-AU How to program ATmega8 using USBasp?
To program an ATmega8 microcontroller using USBasp, follow these steps:
- Connect the USBasp programmer to your computer via USB.
- Connect the USBasp programmer to the ATmega8 microcontroller using the appropriate connections (MISO, MOSI, SCK, RESET, and VCC/GND).
- Install the USBasp driver software on your computer if required.
- Open the programming software, such as AVRDUDE, in the command line or use a graphical interface like AVR Studio or Arduino IDE.
- Specify the USBasp programmer as the programming device and select the appropriate settings for the ATmega8 microcontroller (e.g., clock frequency, fuse settings).
- Load the compiled program (hex file) into the programming software.
- Start the programming process, which will upload the program to the ATmega8 microcontroller using the USBasp programmer.
ATMega8A vs ATMega328p
The ATmega8A and ATmega328P are both microcontrollers from the AVR family, but they have several differences:
- Flash Memory: The ATmega8A has 8 KB of Flash memory, while the ATmega328P has 32 KB.
- SRAM: The ATmega8A has 1 KB of SRAM, whereas the ATmega328P has 2 KB.
- EEPROM: The ATmega8A has 512 bytes of EEPROM, while the ATmega328P has 1 KB.
- I/O Pins: The ATmega8A has 23 general-purpose I/O pins, while the ATmega328P has 23 or 28, depending on the package variant.
- Timers/Counters: The ATmega8A has three 8-bit timers/counters, while the ATmega328P has three 16-bit timers/counters.
- Serial Communication: The ATmega8A has a USART for serial communication, while the ATmega328P has a USART and additional support for I2C and SPI.
- Clock Speed: The ATmega8A can operate up to 16 MHz, while the ATmega328P can operate at higher frequencies, such as 20 MHz or with an external crystal up to 32 MHz.
Related articles
ATMEGA1284P-MU Microcontrollers: Datasheet, Distinction
ATMEGA328-PU Effecient 8-Bit Microcontrollers: PDF, Pinout
ATMEGA128A-AU 8-bit AVR Microcontroller Datasheet, Specification
ATMEGA128A-AU vs ATMEGA1284P-MU: Differences and Similarity
ATMEGA2560-16AU VS ATMEGA640-16AU Microcontroller: Difference
atmega8a-au datasheet will displayed in the last two parts
Specifications
- Manufacturer :
- Microchip Technology
- Product Category :
- Microcontrollers
- Additional Feature :
- OPERATES AT 2.7 V MINIMUM SUPPLY AT 8 MHZ
- Base Part Number :
- ATMEGA8A
- Base Product Number :
- ATMEGA8
- Bit Size :
- 8
- Brand :
- Microchip Technology / Atmel
- Connectivity :
- I2C, SPI, UART/USART
- Contact Plating :
- Tin
- Core Architecture :
- AVR
- Core Processor :
- AVR
- Core Size :
- 8-Bit
- CPU Family :
- AVR RISC
- DAC Channels :
- No
- Data Bus Width :
- 8B
- Data Converter :
- A/D 8x10b
- Data Converters :
- A/D 8x10b
- Device Core :
- AVR
- Dimensions :
- 7.1 x 7.1 x 1.05mm
- DMA Channels :
- No
- EEPROM Size :
- 512 x 8
- Enclosure :
- TQFP 32 (7x7)
- Factory Lead Time :
- 6 Weeks
- Family Name :
- ATMEGA
- Frequency :
- 16MHz
- Has ADC :
- yes
- Height :
- 1.05mm
- Instruction Set Architecture :
- RISC
- Interface :
- I2C, SPI, UART, USART
- Interface Type :
- SPI, TWI, USART
- Interfaces :
- SPI/TWI/USART
- JESD-30 Code :
- S-PQFP-G32
- JESD-609 Code :
- e3
- Lead Free :
- Lead Free
- Length :
- 7mm
- Lifecycle Status :
- Production (Last Updated: 2 years ago)
- Manuf. code :
- MCP
- Manufacturer :
- Microchip Technology
- Max Frequency :
- 16 MHz
- Max Operating Temperature :
- 85 °C
- Max Supply Voltage :
- 5.5 V
- Max. operating temperature :
- +85°C
- Maximum Operating Temperature :
- +85 °C
- Memory Size :
- 8kB
- Memory Type :
- Flash
- Mfr :
- Microchip Technology
- Min Operating Temperature :
- -40 °C
- Min Supply Voltage :
- 2.7 V
- Minimum Operating Temperature :
- -40 °C
- Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) :
- 3 (168 Hours)
- Mount :
- Surface Mount
- Mounting Style :
- SMD/SMT
- Mounting Type :
- Surface Mount
- MSL :
- MSL 3 - 168 hours
- Number of ADC Channels :
- 8
- Number of I/O :
- 23
- Number of I/O Lines :
- 23
- Number of I/Os :
- 23 I/O
- Number of I2C Channels :
- 1
- Number of Pins :
- 32
- Number of Programmable I/O :
- 23
- Number of PWM Channels :
- 3
- Number of SPI Channels :
- 1
- Number of Terminals :
- 32
- Number of Terminations :
- 32
- Number of Timers/Counters :
- 3 Timer
- Operating Temperature :
- -40°C~85°C TA
- Oscillator Type :
- Internal
- Package :
- Tray
- Package / Case :
- 32-TQFP
- Package Shape :
- Square
- Package Type :
- TQFP
- Packaging :
- Tray
- Part Status :
- Active
- Pbfree Code :
- yes
- Peak Reflow Temperature (Cel) :
- 260
- Peripherals :
- Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
- Pin Count :
- 32
- Power Supplies :
- 3/5 V
- Product :
- MCU
- Product Category :
- 8-bit Microcontrollers - MCU
- Product Status :
- Active
- Product Type :
- 8-bit Microcontrollers - MCU
- Program Memory Size :
- 8KB 4K x 16
- Program Memory Type :
- Flash
- Published :
- 2009
- PWM Channels :
- yes
- Qualification :
- -
- Qualification Status :
- Not Qualified
- Radiation Hardening :
- No
- RAM (bytes) :
- 1024
- RAM Size :
- 1K x 8
- Reach Compliance Code :
- Compliant
- REACH SVHC :
- No SVHC
- RoHS :
- Details
- RoHS Status :
- ROHS3 Compliant
- ROM (words) :
- 4096
- ROM Programmability :
- Flash
- Schedule B :
- 8542310000
- Seated Height-Max :
- 1.2 mm
- Series :
- AVR® ATmega
- Speed :
- 16MHz
- Supplier Device Package :
- 32-TQFP (7x7)
- Supply Current-Max :
- 15 mA
- Supply Voltage :
- 5V
- Supply Voltage-Max (Vsup) :
- 5.5V
- Supply Voltage-Min (Vsup) :
- 4.5V
- Surface Mount :
- yes
- Temperature Grade :
- Industrial
- Terminal Finish :
- Matte Tin (Sn)
- Terminal Form :
- Gull wing
- Terminal Pitch :
- 0.8 mm
- Terminal Position :
- QUAD
- Time@Peak Reflow Temperature-Max (s) :
- 40
- Tradename :
- AVR
- Type :
- ATMEGA8A-AU
- Typical Operating Supply Voltage :
- 2.7 → 5.5 V
- uPs/uCs/Peripheral ICs Type :
- MICROCONTROLLER, RISC
- Voltage - Supply (Vcc/Vdd) :
- 2.7V~5.5V
- Watchdog Timer :
- yes
- Width :
- 7mm
Datasheets
- Datasheets
- ATMEGA8A-AU
Product comparison
-
ImagePart NumberManufacturerToleranceVoltage - RatedProduct StatusPackage / CaseProduct CategoryView Compare
-
-
-
Active
28-DIP (0.300, 7.62mm)
Microcontrollers
-
-
-
Active
32-TQFP
Microcontrollers
-
-
-
Active
32-TQFP
Microcontrollers
-
-
-
Active
32-VFQFN Exposed Pad
Microcontrollers

Frequently Asked Questions
What is ATmega8?
1. What is ATmega8? ATmega8 is a popular 8-bit microcontroller from the AVR family manufactured by Microchip Technology (formerly Atmel). It offers a range of features and is widely used in various embedded systems and DIY projects due to its versatility and ease of use.
What is the difference between ATmega8 and ATmega8A?
The ATmega8 and ATmega8A microcontrollers are very similar, but there are a few differences between them. The primary difference lies in the manufacturing process. The ATmega8A is a later revision of the ATmega8 and offers improved characteristics such as lower power consumption and enhanced accuracy.
What is the difference between ATmaega8 and Atmega328?
The ATmega8 and ATmega328 are both microcontrollers from the AVR family, but they have significant differences. The ATmega328 is a more advanced version compared to the ATmega8. It offers higher flash memory (32 KB compared to 8 KB in ATmega8), more SRAM (2 KB compared to 1 KB), and additional features such as more I/O pins, more timers, and built-in support for serial communication protocols like I2C and SPI.
How to burn bootloader in ATmega8A?
To burn the bootloader in an ATmega8A microcontroller, you typically need an external programmer such as the USBasp or AVRISP. Here are the general steps to follow: - Connect the programmer to your computer and the ATmega8A microcontroller. - Open the Arduino IDE and select the appropriate board (e.g., Arduino NG or older w/ ATmega8) and programmer (e.g., USBasp) from the Tools menu. - Choose the appropriate port and then select "Burn Bootloader" from the Tools menu. - The IDE will compile the bootloader code and upload it to the ATmega8A microcontroller using the programmer.
How to program AVR microcontroller using Arduino?
To program an AVR microcontroller using Arduino, follow these steps: - Connect your AVR microcontroller to your computer via a suitable programmer (e.g., USBasp, AVRISP, Arduino as ISP) or use an Arduino board itself as a programmer. - Launch the Arduino IDE and open the sketch (program) you want to upload to the AVR microcontroller. - Select the appropriate board from the Tools menu (e.g., Arduino Uno for ATmega328). - Choose the correct programmer from the Tools menu (e.g., USBasp). - Select the appropriate port. - Click on the "Upload" button or select "Upload Using Programmer" from the Sketch menu to compile and upload the sketch to the AVR microcontroller.
What is the specification of ATmega8A?
You could refer the specification as well as datasheet of ATmega8A in the article.
What is atmega8a-au price in india
-
1,000+Daily Order Quantity
-
2,500,000+Alternative Parts
-
2,200+Worldwide Manufacturers
-
10,000 ㎡In-stock Warehouse