Comparison between RP2040, ESP8266, ESP32, STM32: Pinout
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32
128KB 128K x 8 FLASH ARM® Cortex®-M3 32-Bit Microcontroller STM32F1 Series STM32F103 48 Pin 72MHz 3.3V 48-LQFP
RP2040, ESP8266, ESP32, and STM32 are all microcontrollers. This article is going to talk about the detailed information about RP2040, ESP8266, ESP32, and STM32, and interpret the differences between them.
What is simple definition of microcontroller ?
RP2040 Overview & Features
ESP8266 Overview & Features
ESP32 Overview & Features
STM32 Overview & Features
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 PinoutRP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Block Diagram
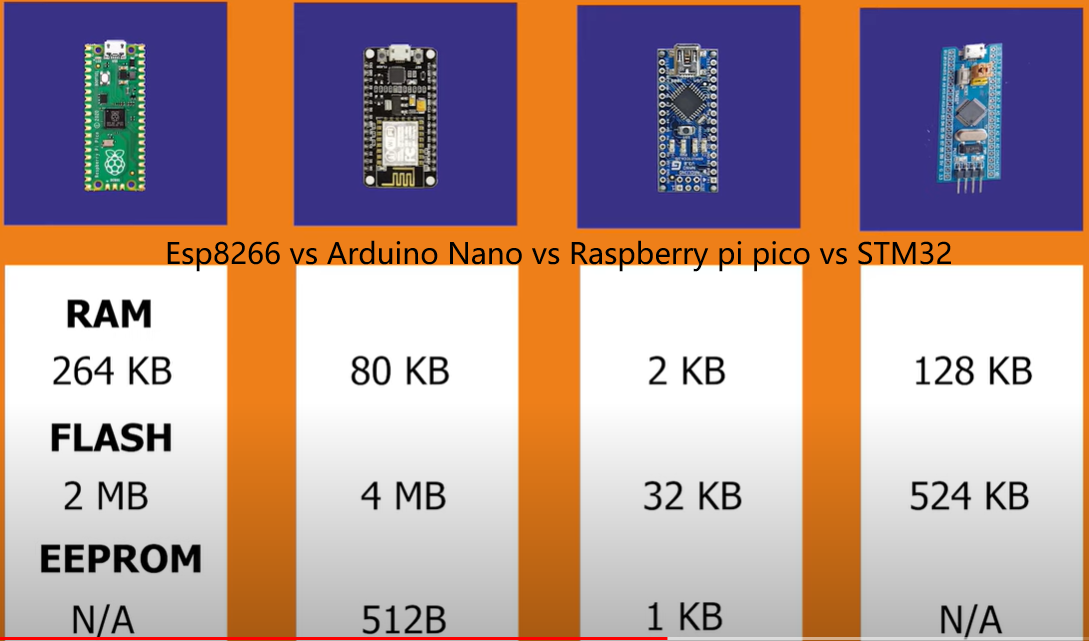
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Parameters
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Datasheet
Conclusion of RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32
What is simple definition of microcontroller ?
First of all, we need to know what microcontroller is.
A microcontroller is a small computer on a single integrated circuit (IC) that contains a processor core, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals. It is designed to perform specific tasks and control electronic devices. Microcontrollers are widely used in various applications, such as embedded systems, robotics, home automation, and industrial control systems. They are programmed to execute specific instructions and interact with external components to perform desired functions. Popular microcontroller families include Arduino, Raspberry Pi, PIC, and STM32.
Overview of RP2040
The RP2040 is a stateless device that uses external QSPI memory to cache execute-in-place capability. This design decision enables you to select the best nonvolatile storage density for your application while taking advantage of commodity Flash's low pricing. The RP2040 is built on a cutting-edge 40nm process node, which provides exceptional performance, low dynamic power consumption, and little leakage, as well as a range of low-power modes for extended battery life. The RP2040 provides professional customers with unrivaled power and flexibility thanks to its huge on-chip memory, symmetric dual-core processing complex, deterministic bus fabric, and complete peripheral set reinforced with our innovative Programmable I/O (PIO) subsystem.
RP2040 Features
• Dual ARM Cortex-M0+ @ 133MHz
• 264kB on-chip SRAM in six independent banks
• Support for up to 16MB of off-chip Flash memory via dedicated QSPI bus
• DMA controller
• Fully-connected AHB crossbar
• Interpolator and integer divider peripherals
• On-chip programmable LDO to generate a core voltage
• 2 on-chip PLLs to generate USB and core clocks
• 30 GPIO pins, 4 of which can be used as analog inputs
• Peripherals
Overview of ESP8266
A Tensilica 32-bit processor, standard digital peripheral interfaces, antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low noise receive amplifier, filters, and power management modules are all built within the ESP8266. They're all bundled together in one compact packet.
Because of its wide operating temperature range, the ESP8266 can perform reliably in industrial settings. The chip provides dependability, compactness, and robustness because of highly integrated on-chip functionalities and a low number of external discrete components.
The Tensilica L106 32-bit RISC processor of the ESP8266 microcontroller consumes very little power and runs at a maximum clock speed of 160 MHz. About 80% of the processing power is accessible for user application programming and development thanks to the Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) and Wi-Fi stack.
ESP8266 Features
802.11 b/g/n support
802.11 n support (2.4 GHz), up to 72.2 Mbps
Defragmentation
2 x virtual Wi-Fi interface
Automatic beacon monitoring (hardware TSF)
Support Infrastructure BSS Station mode/SoftAP mode/Promiscuous mode
Overview of ESP32
ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system on a chip (SoC) series with Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth features developed by Espressif Systems! The chips ESP32-D0WDQ6 (and ESP32-D0WD), ESP32-D2WD, ESP32-S0WD, and the system in package (SiP) ESP32-PICO-D4 are all part of the ESP32 family. A dual-core or single-core Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor with a clock rate of up to 240 MHz is at its heart. Antenna switches, RF baluns, power amplifiers, low-noise receive amplifiers, filters, and power management modules are all included in the ESP32. ESP32 is designed for mobile devices, wearable electronics, and IoT applications, and it uses power-saving technologies including fine resolution clock gating, numerous power modes, and dynamic power scaling to achieve ultra-low power consumption.
ESP32 Features
Processors:
CPU: Xtensa dual-core (or single-core) 32-bit LX6 microprocessor, operating at 160 or 240 MHz and performing at up to 600 DMIPS
Ultra-low-power (ULP) co-processor
Memory: 320 KiB RAM, 448 KiB ROM
Wireless connectivity:
Wi-Fi: 802.11 b/g/n
Bluetooth: v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE (shares the radio with Wi-Fi)
Peripheral interfaces:
34 × programmable GPIOs
12-bit SAR ADC up to 18 channels
2 × 8-bit DACs
10 × touch sensors (capacitive sensing GPIOs)
4 × SPI
2 × I²S interfaces
2 × I²C interfaces
3 × UART
SD/SDIO/CE-ATA/MMC/eMMC host controller
SDIO/SPI slave controller
Ethernet MAC interface with dedicated DMA and planned IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol support[4]
CAN bus 2.0
Infrared remote controller (TX/RX, up to 8 channels)
Motor PWM
LED PWM (up to 16 channels)
Hall effect sensor
Ultra-low-power analog pre-amplifier
Overview of STM32
STMicroelectronics' STM32 32-Bit ARM® Cortex®-M MCUs are based on the Arm Cortex-M processor and are designed to provide MCU users with new levels of freedom. A 32-bit version of the MCUs is available, which combines high performance, real-time capability, digital signal processing, and low-power, low-voltage operation. This is done while maintaining complete integration and development simplicity.
Arm Cortex-M cores (M0, M0+, M3, M4, and M7), as well as other options, are now available in the STM32 series. This gives developers the option of selecting the optimal STM32 for their needs. The ability to transfer apps from one device to another receives specific attention. Binary compatibility, combined with equivalent pinout assignment, hardware IP proliferation, and a higher-level programming language, are all advantages of the STM32 series.
STM32 Features
• ARM® 32-bit Cortex®-M3 CPU Core
• Memories
• Clock, reset and supply management
• Low-power
• 2 x 12-bit, 1 µs A/D converters (up to 16 channels)
• DMA
• Up to 80 fast I/O ports
• Debug mode
• 7 timers
• Up to 9 communication interfaces
• CRC calculation unit, 96-bit unique ID
• Packages are ECOPACK®
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Pinout

RP2040 Pinout

ESP8266 Pinout

ESP32 Pinout
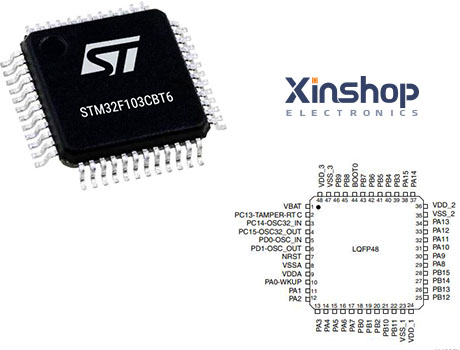
STM32 Pinout
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Block Diagram
![a512ad93b5e690a9726bdaee82ee126d.png IB02MWG{)_J~]%3DI5Q5DTM](/upload/image/content/20230926/a512ad93b5e690a9726bdaee82ee126d.png)
RP2040 Block Diagram
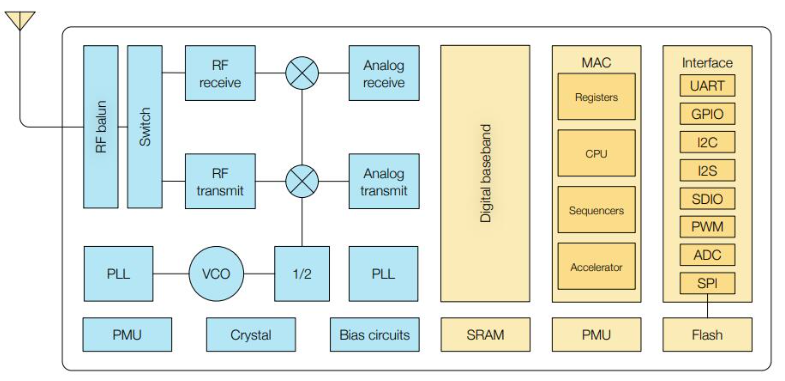
ESP8266 Block Diagram
![9779a451c6f6c51b51813231e1816f0e.png SRT6I3L}X[PA3J]BN@@HY]C](/upload/image/content/20230926/9779a451c6f6c51b51813231e1816f0e.png)
ESP32 Block Diagram

STM32 Block Diagram
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Parameters
RP2040 | ESP32 | STM32F103C8T6 | ESP8266 | |
Release date | 2021 Jan 21 | 2016 | 2014 | |
CPU | Arm Cortex-M0+ Dual-core @133MHz | Tensilica Xtensa LX6 32 bit Dual-Core @ 160 / 240Mhz | 32-bit ARM Cortex M3 72MHz max | Tensilica LX106 32 bit @ 80 MHz (up to 160 MHz) |
Coprocessor | ULP | |||
RAM | 264 KB | 520 KB | 20 kb | 160 KB (36 KB available to user) |
ROM (Flash) | 448 KB | |||
UART | 2 | 3 | 3 USARTs (ISO 7816 interface, LIN, IrDA capability, modem control | 2 |
SPI | Yes 2 (OSPI) | Yes 4 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 |
Wi-Fi | No | Yes 802.11b/g/n | Yes 802.11b/g/n (max 65Mbps) | |
Bluetooth® | No | Yes 4.2 BR/EDR + BLE | No | |
USB Host | Yes | No | No | |
Ethernet (LAN, RJ45) | No | Yes 10/100Mbps | No | |
RTC Memory | 16 KB | |||
External SPIRAL | 16 MB up to | 16 MB up to | ||
External Flash | ||||
ESP-MESH | No | Yes | Yes | |
CAN | Yes v2.0 | |||
GPIO | 30 | 32 (up to) | 17 (up to) | |
Hall effect sensor | No | Yes | No | |
Temperature sensor | No | Yes | No | |
Touch sensors | 10 | No | ||
I²C | Yes | Yes up to 2 | Yes up to 2 | Yes up to 1 |
I2S | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
ADC | Yes x4 12-bit | Yes 12 bit SAR ADC up to 18 channels | Yes 2 x 12-bit, 1 μs A/D converters (up to 16 channels) | Yes 10 bit |
DAC | No | Yes 8 bit up to 2 channels | No | No |
PWM | Yes up to 16 | Yes up to 8 | Yes 37 | No |
SDMMC | No | Yes | No | |
RMT (remote control) | No | Yes | No | |
LCD Interface | No | No | No | |
Camera Interface | No | No | No | |
Deep sleep consumption | 18 µA (Dormant) 39 µA (Sleep) | 10 µA | 20 µA | |
Security | ||||
Secure flash | 1024-bit OTP secure boot | |||
Cryptography support | AES, SHA-2, RSA, ECC, RNG | |||
Dimensions | ||||
Height | 0.27559 in (7 mm) | 0.23622 in (6 mm) |
| 0.19685 in (5 mm) |
Width | 0.27559 in (7 mm) | 0.23622 in (6 mm) |
| 0.19685 in (5 mm) |
RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32 Datasheet
RP2040 Datasheet
ESP8266 Datasheet
ESP32 Datasheet
STM32 Datasheet
Conclusion of RP2040 VS ESP8266 VS ESP32 VS STM32
ESP32 VS ESP8266: ESP32 is better than ESP8266 because ESP32 has extra features such as a CPU core, Faster Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.0 (BLE), touch sensitivity pins, and built-in Hall Effect sensors and temperature sensors. The ESP32 has more GPIO pins as compared to the ESP8266. The ESP32 contains 10 capacitive GPROS that detect touch and can be used to trigger events. The trigger event is a circuit in which action is initiated by an input pulse e.g. as in a radar module. The ESP8266 is a less expensive alternative to the ESP32. Although it lacks several features, it suffices for the majority of simple DIY IoT projects. However, the GPIO mapping has some limits, and there may not be enough pins for what you want to achieve. If that's the case, an ESP32 is the way to go.
RP2040 VS ESP32: The Raspberry Pi Pico is a beginner-friendly microcontroller board that uses MicroPython to give you a taste of the Internet of Things and microcontrollers. The RP2040 is a well-designed microprocessor that can be utilized in almost any Internet of Things project. It has enough power to complete the task quickly. The dual-core processor's CPU type is ARM M0+. For roughly $4, you get all of these features, which is a great deal for students who want to board for a range of tasks that don't require internet access. On the other side, the ESP 32 is a compact but capable microcontroller board. Because of its low cost, low power consumption, and tiny size, it is a well-developed microprocessor that may be used in a range of IoT applications.
RP2040 VS ESP32 VS STM32: On the other side, the ESP 32 is a compact but capable microcontroller board. Because of its low cost, low power consumption, and tiny size, it is a well-developed microprocessor that may be used in a range of IoT applications. Because of its wireless connectivity and other intriguing features, this microcontroller board has acquired a reputation as one of the top boards for IoT developers. The RP2040 is a well-designed microprocessor that can be utilized in almost any Internet of Things project. On the other side, the ESP 32 is a compact but capable microcontroller board. Because of its low cost, low power consumption, and tiny size, it is a well-developed microprocessor that may be used in a range of IoT applications.

Frequently Asked Questions


















