
1N4448 vs 1N4148 Fast Switching Diode: Datasheet
yunying Release time:2023-09-28 Page View:805

Introduction
![56df3a9fb70733f8e495163eee05a942.png 4U6QN}OB_0F24U4AWLD]O~G](https://www.xinshop.com/upload/image/content/20230928/56df3a9fb70733f8e495163eee05a942.png)
Fast switching diodes are essential components in electronic circuits, enabling efficient rectification, signal detection, and protection. Among the popular choices in this category are the 1N4448 diodes and 1N4148 diodes. While these diodes share many similarities, they also possess distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. In this article, we will compare the 1N4448 and 1N4148 diodes, highlighting their differences and helping you make an informed decision when selecting the appropriate diode for your circuit.
What is 1N4448?
* 1N4448 Pinout

* 1N4448 CAD-Model
Symbol

Footprint

3D-model

* 1N4448 Features
- Fast-switching diode similar to 1N4148.
- Higher peak repetitive reverse voltage: 150V.
- Forward continuous current: 300mA.
- Fast recovery time.
- Suitable for applications requiring a higher voltage rating.
* 1N4448 Applications
- **1N4448 Applications:**
- High-speed switching applications.
- Voltage clamping.
- Signal rectification.
- Fast recovery applications.
- Circuit protection.
* 1N4448 Package

What is 1N4148?
* 1N4148 Pinout

* 1N4148 CAD-Model
Symbol

Footprint

3D-model

*1N4148 Features
- **1N4148 Features:**
- General-purpose silicon switching diode.
- Fast-switching speed.
- Peak repetitive reverse voltage: 100V.
- Forward continuous current: 300mA.
- Low forward voltage drop.
- Small signal diode suitable for signal and general-purpose applications.
*1N4148 Applications
- **1N4148 Applications:**
- Signal rectification.
- Clipping and switching applications.
- Voltage spike suppression.
- General-purpose diode applications.
* 1N4148 Package

* 1N4448 Diode Equivalent and 1N4148 Diode Equivalent
- The 1N4148 and 1N4448 are equivalent diodes with slight variations in their voltage ratings. In many applications, they can be used interchangeably depending on the specific voltage requirements of the circuit.
- Some equivalent diodes to 1N4148 and 1N4448 include 1N914, 1N914B, BA85, 1N914C, and BA85-02.
1N4448 vs 1N4148 Difference
Forward Voltage Drop
The forward voltage drop is a crucial parameter to consider when choosing a diode. The 1N4448 diode typically exhibits a lower forward voltage drop compared to the 1N4148. This means that the 1N4448 diode will have a slightly lower
voltage drop when conducting current. This characteristic can be advantageous in circuits where minimizing voltage losses is crucial.
Reverse Recovery Time
The reverse recovery time is another critical factor to consider, especially in high-speed switching applications. The 1N4448 diode boasts a faster reverse recovery time compared to the 1N4148. This means that
it can swiftly transition from the conducting state to the blocking state when the polarity of the applied voltage changes. The faster reverse recovery time of the 1N4448 makes it suitable for applications that demand rapid switching and high-frequency operation.
Power Dissipation
Power dissipation is an important consideration to ensure the diode can handle the required power levels without getting damaged.
In this aspect, the 1N4448 diode outperforms the 1N4148. The 1N4448 can withstand slightly higher power dissipation compared to the 1N4148. This characteristic makes the 1N4448 diode more suitable for applications where higher power levels need to be handled.
Working principle
How do 1N4448 vs 1N4148 work? Both the 1N4448 and 1N4148 operate based on the principles of semiconductor junction behavior.
In forward bias, when the anode (P-type side) is at a higher potential than the cathode (N-type side), current can flow through the diode. The PN junction allows current to pass, as the excess positive charges in the P-type material attract the negatively charged electrons from the N-type material. This creates a current flow from the anode to the cathode.
In reverse bias, with the anode at a lower potential than the cathode, the PN junction acts as an insulator and restricts the flow of current. The depletion region widens, creating a high resistance barrier that prevents most of the current from passing through.
Both diodes are commonly used for signal rectification, switching, and protection purposes. They allow current to flow in one direction (from anode to cathode) while blocking current in the opposite direction. This property makes them suitable for converting AC signals into pulsating DC signals and for various electronic applications.
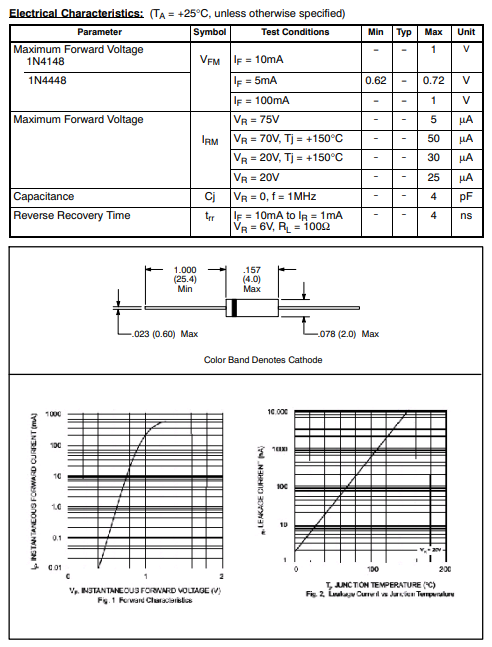
1N4448 vs 1N4148 Datasheet
Please swipe to the last two part for Downloading 1N4448 pdf, 1N4148 Datasheet, 1N4448 vs 1N4148 specifications and product comparison.
1N4448 vs 1N4148 PDF

Conclusion
Both the diode 1N4448 and diode1N4148 fast switching diodes are widely used in electronic circuits. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the circuit and the desired performance characteristics. If minimizing voltage drops and achieving faster switching speeds are crucial, the 1N4448 signal diode would be a suitable choice. On the other hand, if power dissipation is a concern, the 1N4148 signal diode can handle slightly higher power levels. It is important to carefully analyze the circuit requirements and select the appropriate diode to ensure optimal performance.
Specifications
- Manufacturer :
- onsemi
- Product Category :
- Diodes - Rectifiers - Single
- Average Rectified Current :
- 200mA
- Base Part Number :
- 1N4448
- Capacitance :
- 2pF
- Capacitance @ Vr, F :
- 2pF @ 0V 1MHz
- Contact Plating :
- Tin
- Current :
- 2A
- Current - Average Rectified (Io) :
- 200mA
- Current - Reverse Leakage @ Vr :
- 5μA @ 75V
- Current Rating :
- 200mA
- Diode Type :
- Standard
- Element Configuration :
- Single
- Factory Lead Time :
- 18 Weeks
- Forward Current :
- 300mA
- Forward Voltage :
- 1V
- Height :
- 1.91mm
- Lead Free :
- Lead Free
- Length :
- 4.56mm
- Lifecycle Status :
- ACTIVE (Last Updated: 1 day ago)
- Max Forward Surge Current (Ifsm) :
- 4A
- Max Junction Temperature (Tj) :
- 175°C
- Max Operating Temperature :
- 175°C
- Max Power Dissipation :
- 500mW
- Max Repetitive Reverse Voltage (Vrrm) :
- 100V
- Max Reverse Voltage (DC) :
- 100V
- Max Surge Current :
- 4A
- Min Operating Temperature :
- -55°C
- Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) :
- 1 (Unlimited)
- Mount :
- Through Hole
- Mounting Type :
- Through Hole
- Number of Pins :
- 2
- Operating Temperature - Junction :
- -65°C~175°C
- Output Current :
- 200mA
- Package / Case :
- DO-204AH, DO-35, Axial
- Packaging :
- Bulk
- Part Status :
- Active
- Peak Non-Repetitive Surge Current :
- 4A
- Peak Reverse Current :
- 5μA
- Polarity :
- Standard
- Power Dissipation :
- 500mW
- Published :
- 2016
- Radiation Hardening :
- No
- REACH SVHC :
- No SVHC
- Recovery Time :
- 4 ns
- Reverse Recovery Time :
- 4 ns
- RoHS Status :
- ROHS3 Compliant
- Speed :
- Small Signal =< 200mA (Io), Any Speed
- Supplier Device Package :
- DO-35
- Voltage :
- 75V
- Voltage - DC Reverse (Vr) (Max) :
- 100V
- Voltage - Forward (Vf) (Max) @ If :
- 1V @ 100mA
- Voltage - Rated DC :
- 100V
- Weight :
- 126.01363mg
- Width :
- 1.91mm
Datasheets
- Datasheets
- 1N4448

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between 1N4148 and 1N4448?
The main difference between 1N4148 and 1N4448 is the peak repetitive reverse voltage rating, with 1N4448 having a higher voltage rating. 1N4148: It is a general-purpose silicon switching diode with a peak repetitive reverse voltage rating of 100V. It is commonly used in signal and general-purpose applications. 1N4448: It is also a fast-switching diode but with a slightly higher peak repetitive reverse voltage rating of 150V. This makes it suitable for applications that require a higher voltage rating compared to the 1N4148.
What is the difference between 1N4148 and 1N4149?
The 1N4148 and 1N4149 are both fast-switching diodes as well, and the key differences between them are: 1N4148: As mentioned earlier, the 1N4148 is a general-purpose silicon switching diode with a peak repetitive reverse voltage rating of 100V. 1N4149: The 1N4149 is very similar to the 1N4148 but with a higher peak repetitive reverse voltage rating of 200V. This higher voltage rating makes it suitable for applications that require a higher voltage tolerance compared to the 1N4148. In summary, the main difference between 1N4148 and 1N4149 is the peak repetitive reverse voltage rating, with 1N4149 having a higher voltage rating.
-
1,000+Daily Order Quantity
-
2,500,000+Alternative Parts
-
2,200+Worldwide Manufacturers
-
10,000 ㎡In-stock Warehouse


























