
Overview For ADS774JU Analog to Digital Converters: How it Works
yunying Release time:2024-01-16 Page View:216
Analog to Digital Converters - ADC Mcrprcsr-Compatible Sampling CMOS
Introduction
The ADS774JU is a high-performance Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) manufactured by Texas Instruments. It is part of the ADS77x family of ADCs, which are known for their exceptional accuracy and precision. With its advanced features and versatile applications, the ADS774JU is a popular choice among engineers working on various electronic projects. This article provides a detailed description of the ADS774JU, highlighting its features, applications, pinout, and alternative options.
ADS774JU Description

The ADS774JU is a 16-bit successive approximation register (SAR) ADC that offers excellent performance in terms of resolution and sampling rate. It provides a single-ended input configuration and operates with a wide supply voltage range of 4.5V to 5.5V. The ADC uses a differential input architecture, allowing for high common-mode rejection and low distortion. The ADS774JU also incorporates a built-in reference voltage generator, eliminating the need for an external reference source.
The ADS774 is a 12-bit successive approximation analog-to-digital converter using an innovative capacitor array (CDAC) implemented in low-power CMOS technology. This is a drop-in replacement for ADC574, ADC674, and ADC774 models in most applications, with internal sampling, much lower power consumption, and the ability to operate from a single +5V supply.
The ADS774 is complete with internal clock, microprocessor interface, three-state outputs, and internal scaling resistors for input ranges of 0V to +10V, 0V to +20V, ±5V, or ±10V. The maximum throughput time is 8.5µs over the full operating temperature range, including both acquisition and conversion.
Complete user control over the internal sampling function facilitates elimination of external sample/hold amplifiers in most existing designs.
The ADS774 requires +5V, with –15V optional. No +15V supply is required. Available packages include 0.3" or 0.6" wide 28-pin plastic DIP and 28-pin SOICs.
ADS774JU Pinout
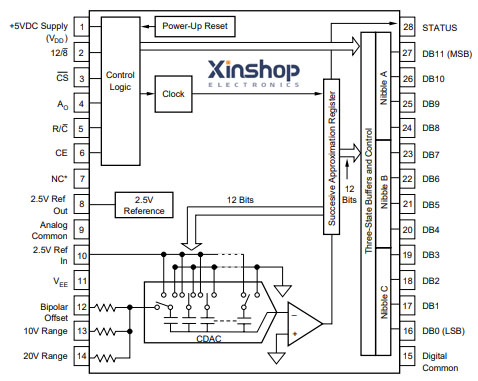
The ADS774JU is available in a small form factor 24-pin TSSOP (Thin Shrink Small Outline Package) package.
ADS774JU CAD-Model
Symbol

Footprint
CAD-Model
ADS774JU Features
1. High Resolution: The ADS774JU offers a 16-bit resolution, allowing for precise and accurate data conversion.
2. Fast Conversion Speed: With a maximum sampling rate of 250 kSPS (thousand samples per second), the ADC can handle high-speed data acquisition requirements.
3. Low Power Consumption: The device operates at a low power consumption level, making it suitable for power-sensitive applications.
4. Low Noise: The ADC exhibits low noise performance, ensuring reliable data conversion in noisy environments.
5. Integrated Reference Voltage: The built-in reference voltage generator simplifies the design and reduces external component requirements.
6. Flexible Input Configuration: The ADC supports single-ended input signals, enabling easy integration with various sensors and analog signal sources.
7. Serial Interface: The ADS774JU utilizes a serial interface (SPI) for communication with microcontrollers or digital systems.
8. Wide Temperature Range: The device operates reliably over a wide temperature range, making it suitable for industrial and automotive applications.
Features
● Replaces Adc574, Adc674 And Adc774 For New Designs
● Complete Sampling A/D With Reference, Clock And Microprocessor Interface
● Fast Acquisition And Conversion: 8.5µs Max Over Temperature
● Eliminates External Sample/Hold In Most Applications
● Guaranteed Ac And Dc Performance
● Single +5V Supply Operation
● Low Power: 120mw Max
● Package Options: 0.6" And 0.3" Dips, Soic
ADS774JU Replacement
Alternatives:
While the ADS774JU offers exceptional performance, there are alternative ADC options available in the market. Some notable alternatives to the ADS774JU include:
1. LTC2508-32: A 32-bit SAR ADC by Analog Devices, known for its high resolution and low power consumption.
2. MAX11131: A 16-bit SAR ADC by Maxim Integrated, featuring low noise, fast conversion speed, and a wide supply voltage range.
3. MCP3551: A 22-bit Delta-Sigma ADC by Microchip, offering high resolution and excellent accuracy.
ADS774JU Application
The ADS774JU finds applications in a wide range of industries and electronic systems, including but not limited to:
1. Industrial Automation: The ADC is used in industrial control systems, data acquisition, and monitoring applications.
2. Medical Devices: It is employed in medical instruments for accurate measurement and monitoring of biological signals.
3. Communication Systems: The ADC is utilized in wireless communication systems, including base stations and wireless transceivers.
4. Test and Measurement Equipment: The device is commonly used in oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and other testing instruments.
5. Automotive Electronics: The ADC is suitable for automotive systems such as engine control units, battery management systems, and sensor interfaces.
Typical Applications
· Scientific instruments
· Rotary encoder
· Displaying
· Transducer
· Microcontrollers.
· Digital Storage Oscilloscope
· Scientific instruments.
· Music reproduction technology
· Communication Systems
· Data Acquisition Systems
ADS774JU Package
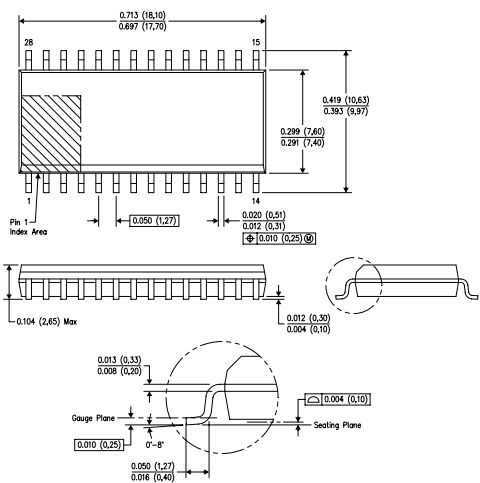
Conclusion
The ADS774JU Analog to Digital Converter is a high-performance device that provides accurate and precise data conversion. With its impressive features, versatile applications, and reliable performance, the ADC is widely used in various industries and electronic systems. Engineers can refer to the datasheet and application notes provided by Texas Instruments for detailed information on integrating the ADS774JU into their designs.
Specifications
- Manufacturer :
- Texas Instruments
- Product Category :
- Analog to Digital Converters (ADC)
- Architecture :
- SAR
- Base Part Number :
- ADS774
- Configuration :
- S/H-ADC
- Contact Plating :
- Gold
- Conversion Rate :
- 125 ksps
- Converter Type :
- ADC, SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION
- Data Interface :
- Parallel
- ECCN Code :
- EAR99
- Factory Lead Time :
- 6 Weeks
- Height :
- 2.65mm
- Input Type :
- Single Ended
- Integral Nonlinearity (INL) :
- 1 LSB
- JESD-609 Code :
- e4
- Lead Free :
- Lead Free
- Length :
- 17.9mm
- Lifecycle Status :
- ACTIVE (Last Updated: 6 days ago)
- Linearity Error-Max (EL) :
- 0.0244%
- Max Power Dissipation :
- 120mW
- Max Supply Voltage :
- 5.5V
- Max Supply Voltage (DC) :
- 5.4V
- Min Supply Voltage :
- 4.5V
- Min Supply Voltage (DC) :
- 4.5V
- Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) :
- 3 (168 Hours)
- Mounting Type :
- Surface Mount
- Negative Supply Voltage-Nom :
- -15V
- Number of Analog In Channels :
- 1
- Number of Bits :
- 12
- Number of Channels :
- 1
- Number of Functions :
- 1
- Number of Pins :
- 28
- Number of Terminations :
- 28
- Operating Supply Voltage :
- 5V
- Operating Temperature :
- -40°C~85°C
- Output Bit Code :
- BINARY, OFFSET BINARY
- Package / Case :
- 28-SOIC (0.295, 7.50mm Width)
- Packaging :
- Tube
- Part Status :
- Active
- Pbfree Code :
- yes
- Peak Reflow Temperature (Cel) :
- 260
- Pin Count :
- 28
- Polarity :
- Bipolar, Unipolar
- Power Consumption :
- 75mW
- Power Dissipation :
- 120mW
- Radiation Hardening :
- No
- Ratio - S/H:ADC :
- 1:1
- REACH SVHC :
- No SVHC
- Reference Type :
- External, Internal
- Resolution :
- 1.5 B
- RoHS Status :
- ROHS3 Compliant
- Sample and Hold / Track and Hold :
- SAMPLE
- Sampling Rate :
- 125 ksps
- Sampling Rate (Per Second) :
- 125k
- Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) :
- 72 dB
- Spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) :
- 78 dB
- Supply Current-Max :
- 24mA
- Supply Type :
- Analog, Digital, Dual, Single
- Supply Voltage :
- 5V
- Surface Mount :
- yes
- Terminal Form :
- Gull wing
- Thickness :
- 2.35mm
- Voltage - Supply, Analog :
- 5V -16.5V~5.5
- Voltage - Supply, Digital :
- 5V
- Width :
- 7.5mm
Datasheets
- Datasheets
- ADS774JU

Frequently Asked Questions
Who invented analog-to-digital converter?
Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) was invented in the late 1950s.Some early developers of ADC technology include several engineers at Bell Labs including Sy Brodsky, Paul M. Rainey, and George Felsenstein. However, the technology became more widely used later in the 1960s as microprocessor systems emerged.
What is the difference between ADC and DAC?
ADC stands for analog-to-digital converter. It is a device that converts continuously varying analog voltage levels to discrete digital numbers that computers can understand and process. ADCs sample an analog input signal, usually at regular intervals, and convert it into a digital code representing the signal amplitude at that instant in time. Digital-to-analog converter (DAC) stands for digital-to-analog converter. It is the opposite of an ADC. A DAC converts digital signal values, usually represented as numbers, into analog waveforms. It takes in digital code as input and outputs a proportional analog voltage or current. DACs are commonly used in applications where a digital system needs to generate an analog output - such as producing sound from a digital audio file, generating an analog radio frequency signal from a digital source, or driving analog circuits or devices with a digital interface. In simple terms, An ADC takes an analog signal and converts it into a binary one, while a DAC converts a binary signal into an analog value.
-
1,000+Daily Order Quantity
-
2,500,000+Alternative Parts
-
2,200+Worldwide Manufacturers
-
10,000 ㎡In-stock Warehouse


























