MPS MP9486AGN-Z: Datasheet, Features
Hi, friends. This post is about MP9486AGN-Z: A Versatile Step-Down Converter IC for Efficient Power Management
Catalog
Introduction
MP9486AGN-Z Overview
MP9486AGN-Z Pinout
MP9486AGN-Z CAD MODEL
MP9486AGN-Z Features and Specifications
MP9486AGN-Z Applications
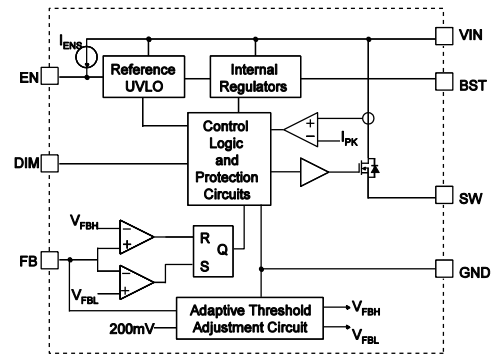
MP9486AGN-Z Block Diagram
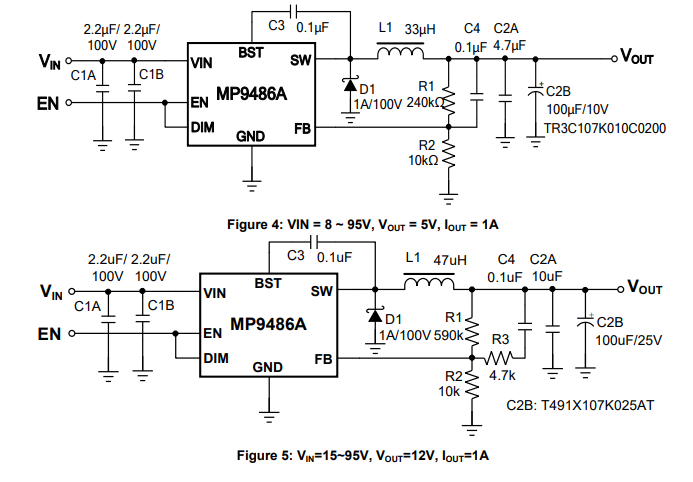
MP9486AGN-Z Circuit
MP9486AGN-Z Price
Conclusion
Introduction:
The MP9486AGN-Z is a highly versatile step-down converter integrated circuit (IC) that offers efficient power management solutions for a wide range of applications. Designed by Monolithic Power Systems (MPS), this IC combines high performance with a compact form factor, making it suitable for various power conversion needs. In this article, we will explore the features, specifications, and potential applications of the MP9486AGN-Z.
MP9486AGN-Z Overview
100V 1A Step-Down Switching Voltage Regulator 8-Pin SOIC.The MP9486A is a high-voltage, step-down switching regulator capable of delivering up to 1A of continuous current to a load. It incorporates a high-side, high-voltage power MOSFET with a usual current limit of 3.5A. The wide input range of 4.5V to 100V enables a wide range of step-down applications, making it perfect for automotive, industrial, and lighting applications. For very quick response, hysteretic voltage-mode control is used. MPS's patented feedback control method reduces the number of external components necessary.
Switching frequencies of up to 1MHz enable for minimal component sizes. Thermal shutdown and short-circuit protection (SCP) ensure that operations are reliable and fault-tolerant. The MP9486A can be employed in battery-powered applications thanks to its 170A quiescent current.
The MP9486A comes in an SOIC-8 box with an exposed pad.
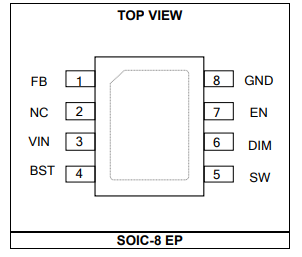
MP9486AGN-Z Pinout
MP9486AGN-Z CAD MODEL
Symbol
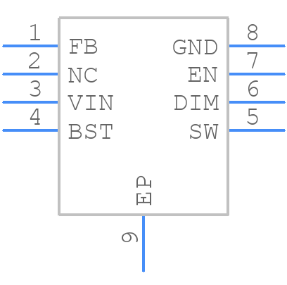
Footprint
3D-Model
Features and Specifications:
The MP9486AGN-Z is a synchronous step-down converter that operates with a wide input voltage range and delivers a regulated output voltage with high efficiency. Some of the key features and specifications of the IC include:
Input Voltage Range: The MP9486AGN-Z supports input voltage ranging from 4.5V to 18V, making it compatible with a variety of power sources, such as batteries, adapters, and industrial power supplies.
Output Voltage Range: The IC provides a configurable output voltage range from 0.6V to 5.5V, allowing flexibility in meeting the requirements of different loads and applications.
High Efficiency: With its synchronous rectification architecture and optimized internal power MOSFETs, the MP9486AGN-Z achieves high efficiency levels, reducing power losses and enhancing overall system efficiency.
Current Mode Control: The IC utilizes a current mode control scheme that provides fast transient response and stable operation across varying load conditions.
Protection Features: The MP9486AGN-Z incorporates a comprehensive set of protection features, including overvoltage protection (OVP), overcurrent protection (OCP), and thermal shutdown, ensuring the safety and reliability of the system.
Applications:
The MP9486AGN-Z finds applications in various electronic systems that require efficient power conversion. Here are a few examples:
Portable Devices: With its wide input voltage range and compact form factor, the MP9486AGN-Z is suitable for powering portable devices like smartphones, tablets, portable gaming consoles, and wearable devices. It provides efficient power conversion, enabling longer battery life and reducing heat dissipation.
Industrial and Automotive Electronics: The IC's robust design and wide input voltage range make it ideal for industrial and automotive applications. It can power sensors, actuators, communication modules, motor control circuits, and other subsystems in industrial automation, automotive infotainment systems, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Networking and Telecommunications: The MP9486AGN-Z can be used in networking and telecommunications equipment, such as routers, switches, and base stations. It efficiently converts the input power to the desired voltage levels required by various components, ensuring stable and reliable operation.
Consumer Electronics: From smart TVs and set-top boxes to audio systems and gaming consoles, the MP9486AGN-Z can be utilized in a range of consumer electronic devices. Its high efficiency and voltage flexibility make it suitable for powering different subsystems within these devices.
MP9486AGN-Z Block Diagram
MP9486AGN-Z Circuit
MP9486AGN-Z Price
Conclusion:
The MP9486AGN-Z is a highly versatile and efficient step-down converter IC that offers power management solutions for a wide range of applications. With its wide input voltage range, high efficiency, and comprehensive protection features, it provides reliable and stable power conversion. Whether used in portable devices, industrial systems, networking equipment, or consumer electronics, the MP9486AGN-Z delivers efficient power management, contributing to enhanced performance and extended battery life. Engineers and designers can leverage the capabilities of the MP9486AGN-Z to optimize power management in their applications, ensuring reliable and energy-efficient operation.
What are the advantages of using a synchronous rectification architecture in the MP9486AGN-Z?
The use of a synchronous rectification architecture in the MP9486AGN-Z step-down converter offers several advantages over conventional diode rectification. Here are some of the key benefits:
Improved Efficiency: Synchronous rectification replaces the diode rectifier with a low-resistance synchronous MOSFET. This MOSFET operates as a switch, turning on and off to direct current flow. By using a controlled switch instead of a diode, synchronous rectification significantly reduces power losses across the rectifier. This leads to improved overall efficiency of the step-down converter. The MP9486AGN-Z leverages this advantage to achieve higher efficiency levels, reducing wasted power and improving energy conversion.
Lower Voltage Drops: Diode rectifiers have inherent voltage drops across them, typically around 0.5V to 1V. These voltage drops cause power dissipation and energy loss. In contrast, synchronous rectification uses MOSFETs with low on-resistance. As a result, the voltage drops across the synchronous MOSFETs are significantly lower than diodes. This leads to higher voltage conversion efficiency and increased available output voltage for the load.
Reduced Heat Dissipation: The lower voltage drops in synchronous rectification result in reduced power dissipation and heat generation compared to diode rectification. As a consequence, the MP9486AGN-Z with synchronous rectification operates at lower temperatures, contributing to improved reliability and longevity of the device. It also reduces the need for additional cooling mechanisms, simplifying thermal management in the system.
Fast Switching Speed: Synchronous rectification MOSFETs have fast switching speeds compared to diodes, allowing for more precise control of the current flow. The MP9486AGN-Z takes advantage of this characteristic to achieve faster transient response and better regulation under varying load conditions. It enables the converter to quickly respond to load changes, maintaining stable output voltage with minimal voltage overshoot or undershoot.
Flexibility in Operating Frequency: Synchronous rectification provides flexibility in choosing the operating frequency of the step-down converter. Unlike diode rectifiers, which have fixed switching frequencies, synchronous rectification allows for higher switching frequencies. This flexibility enables the MP9486AGN-Z to operate at higher frequencies, reducing the size of external components such as inductors and capacitors, and enabling the use of smaller form factors in space-constrained applications.
Compatibility with Light Load Conditions: Diode rectifiers suffer from efficiency degradation at light load conditions due to the fixed voltage drops. In contrast, synchronous rectification maintains high efficiency even at low loads. The MP9486AGN-Z leverages this advantage to provide efficient power conversion across a wide range of load conditions, maximizing energy efficiency in applications that experience varying power demands.
By employing a synchronous rectification architecture, the MP9486AGN-Z step-down converter ensures improved efficiency, lower voltage drops, reduced heat dissipation, fast switching speeds, flexibility in operating frequency, and compatibility with light load conditions. These advantages make it an ideal choice for applications that require high-performance power management with minimal power losses.
How does synchronous rectification affect the size and cost of external components in the MP9486AGN-Z?
Synchronous rectification in the MP9486AGN-Z step-down converter can have an impact on the size and cost of external components in the following ways:
Smaller Inductor: Synchronous rectification allows for higher switching frequencies compared to diode rectification. Higher switching frequencies enable the use of smaller inductors while maintaining the same level of efficiency. Smaller inductors occupy less space on the circuit board, contributing to a more compact overall design. Additionally, smaller inductors tend to be less expensive than larger ones, potentially reducing component costs.
Reduced Output Capacitor Size: The faster switching speeds enabled by synchronous rectification can reduce the required output capacitance. The output capacitor helps smooth out the voltage ripple and stabilize the output voltage. With synchronous rectification, the reduced voltage ripple allows for a smaller output capacitor. This reduction in capacitance value can lead to cost savings and space efficiency.
Elimination of External Schottky Diode: In a synchronous rectification scheme, the need for an external Schottky diode, which is typically used in diode rectification, is eliminated. The low-resistance synchronous MOSFETs replace the diodes, reducing the number of external components required. This simplifies the overall circuit design, reduces component count, and potentially lowers the cost of the system.
Potential for Smaller PCB Size: The combination of smaller inductors, reduced capacitance requirements, and the elimination of external diodes can contribute to a more space-efficient PCB layout. The reduced component count and smaller component sizes associated with synchronous rectification can allow for a more compact design, potentially reducing the size and cost of the overall system.
It's important to note that while synchronous rectification can lead to size and cost reductions in certain external components, the specific impact will depend on the application requirements, desired performance, and the trade-offs made during the design process. It's always recommended to consult the datasheet, application notes, and design guidelines provided by the IC manufacturer to optimize the component selection and achieve the desired balance between size, cost, and performance in the MP9486AGN-Z-based power management system.


















